借助附带流动液体反应池的原位原子力显微镜(AFM),模拟根系分泌的有机酸与土壤难溶性磷矿表面的反应,系统地研究了柠檬酸在各种根际土壤溶液条件下(包括浓度,pH和离子强度)对磷酸氢钙(DCPD)的溶解。我们直接测定了DCPD (010)面不同方向分子级台阶(Figure 2A)溶解速度,结果表明低浓度(100 μM)的柠檬酸,抑制了 [-100]Cc 和 [10-1]Cc两个方向上的台阶移动速度(Figure 2B);然而在高浓度下(大于0.1 mM),柠檬酸的抑制效应转化为促进溶解(Figure 2C)。这些结果说明了柠檬酸对难溶性磷的溶解是由浓度主导的双重调控模式,这为深入理解复杂根际环境下有机酸活化难溶性磷的矿物-水界面反应过程提供了直接微观线索。

Figure 2. (A) AFM deflection image showing the immediate formation of etch pits with triangular shapes on (010) surfaces of a DCPD crystallite
introduced into deionized water or citrate. Retreat velocity of the [-100]Cc steps for DCPD crystals dissolved in (B) low or (C) high citrate concentration solutions at varying pH (4.0-8.0).
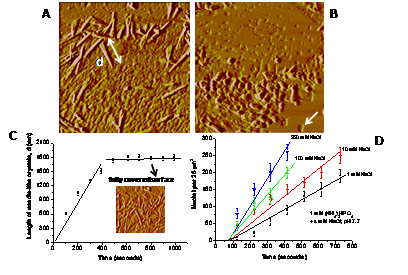
Figure 3. AFM images of the nucleation and growth of (A) needle-shaped or (B) spherical pyromorphite crystals on a dissolving cerussite surface. (C, D) Dependence of the steady-state growth and nucleation rate on time under various solution conditions.
此外,我们利用相似方法研究了可溶性磷如(NH4)2HPO4是如何固定土壤重金属铅的表面化学机制,结果发现铅很容易吸附在碳酸钙表面形成碳酸铅;而可溶性磷溶解碳酸铅后将铅离子释放出来,进而在矿物-水界面层形成针形或球形的磷酸铅(Figure 3A, B)。借助原位原子力显微镜,我们定量地测定了在各种土壤溶液条件下磷酸铅的成核和生长速率(Figure 3C, D)。相关结果系列在线发表在Environmental Science & Technology 上。
(1). Lihong Qin et al., Direct Imaging of Nanoscale Dissolution of Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate by an Organic Ligand: Concentration Matters.
Environmental Science & Technology, DOI: 10.1021/es402748t, 2013.). (IF 5.257)
(2). Lijun Wang et al., Coupled Dissolution and Precipitation at the Cerussite-Phosphate Solution Interface: Implications for Immobilization of Lead in Soils.
Environmental Science & Technology, DOI: 10.1021/es4041946, 2013).